The amount of carbon in the water and the atmosphere is continuing to be a problem in the world around us. The primary effect is on shellfish and microscopic fish, and it has similar effects to osteoporosis in humans. Under the cumulative weight of acidification, warming, habitat destruction, coastal pollution and over-fishing, the ocean environment may soon become fit only for jellyfish.
Why is ocean acidification a problem?
When carbon dioxide dissolves in the ocean, carbonic acid is formed. This leads to higher acidity, mainly near the surface, which has been proven to inhibit shell growth in marine animals and is suspected as a cause of reproductive disorders in some fish.
Ocean Warming
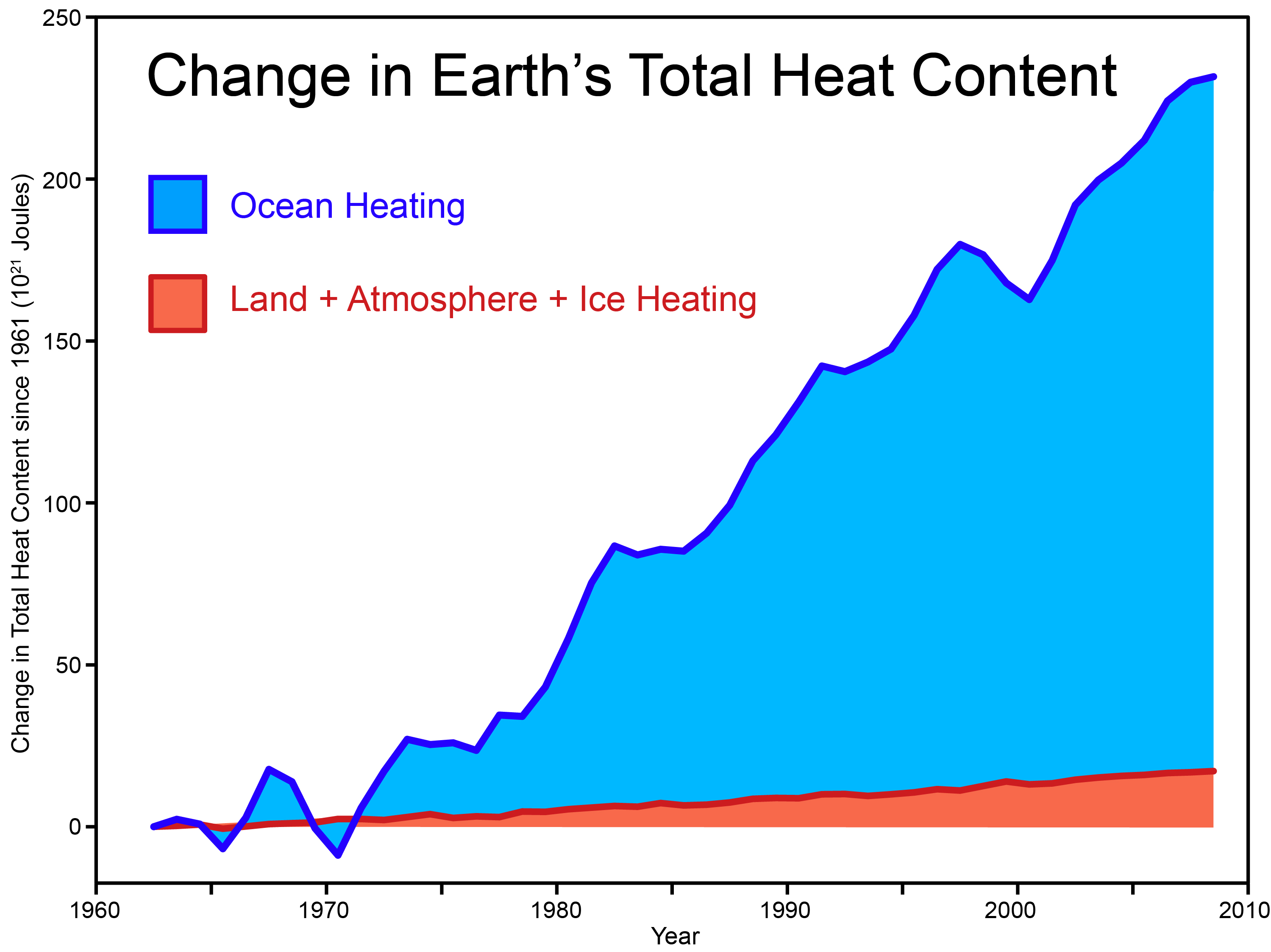
Since 1955, over 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases has been stored in the oceans. The remainder of this energy goes into melting sea ice, ice caps, and glaciers, and warming the continents’s land mass. Only the smallest fraction of this thermal energy goes into warming the atmosphere. Humans thus, living at the interface of the land, ocean and atmosphere, only feel a sliver of the true warming cost of fossil fuel emissions.
Overfishing
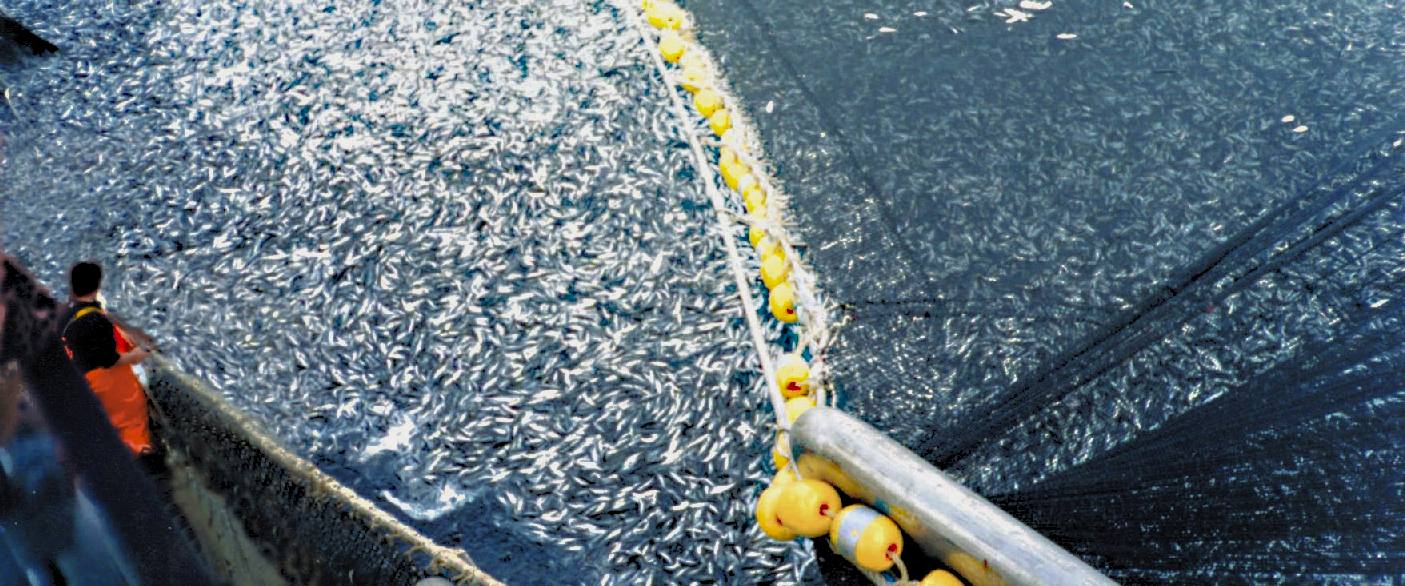

There is much to be desired in the ways we fish. First, we humans use some pretty destructive methods in how we pull catches, including bottom trawling which destroys sea floor habitat and scoops up many unwanted fish and animals that are tossed aside. We also pull far too many fish to be sustainable, pushing many species to the point of being listed as threatened and endangered.Reasons for overfishing are obvious in some ways, in that there are a lot of people who like to eat a lot of fish. The more fish, the more money for the fishermen. However there are other elements at work that promote overfishing that are less obvious, such as promoting the health benefits of one fish over another, or the health of fish oils.
Overfishing is having some serious impacts on our oceans. Not only does it work towards wiping out a species, but also the other species of marine animals that are dependent upon those fish for survival. It’s been shown that overfishing can cause marine animals to starve, since we’re taking food from their mouths in too large of numbers for them to be able to get their fill. It is also estimated that most seas already need long term fishing bans if certain species are to recover at all.
Knowledge of what seafood can be sustainably eaten, whether that is the species of seafood or the method by which it is caught, is a must in order to help keep the ocean’s fisheries healthy. It’s our job as eaters to question restaurant servers, sushi chefs, and seafood purveyors about the sources of their fish, and read labels when we buy from store shelves. Our sustainable seafood slideshows that will show you what you want to look for when you’re choosing your next meal, and what to avoid.
Habitat Destruction
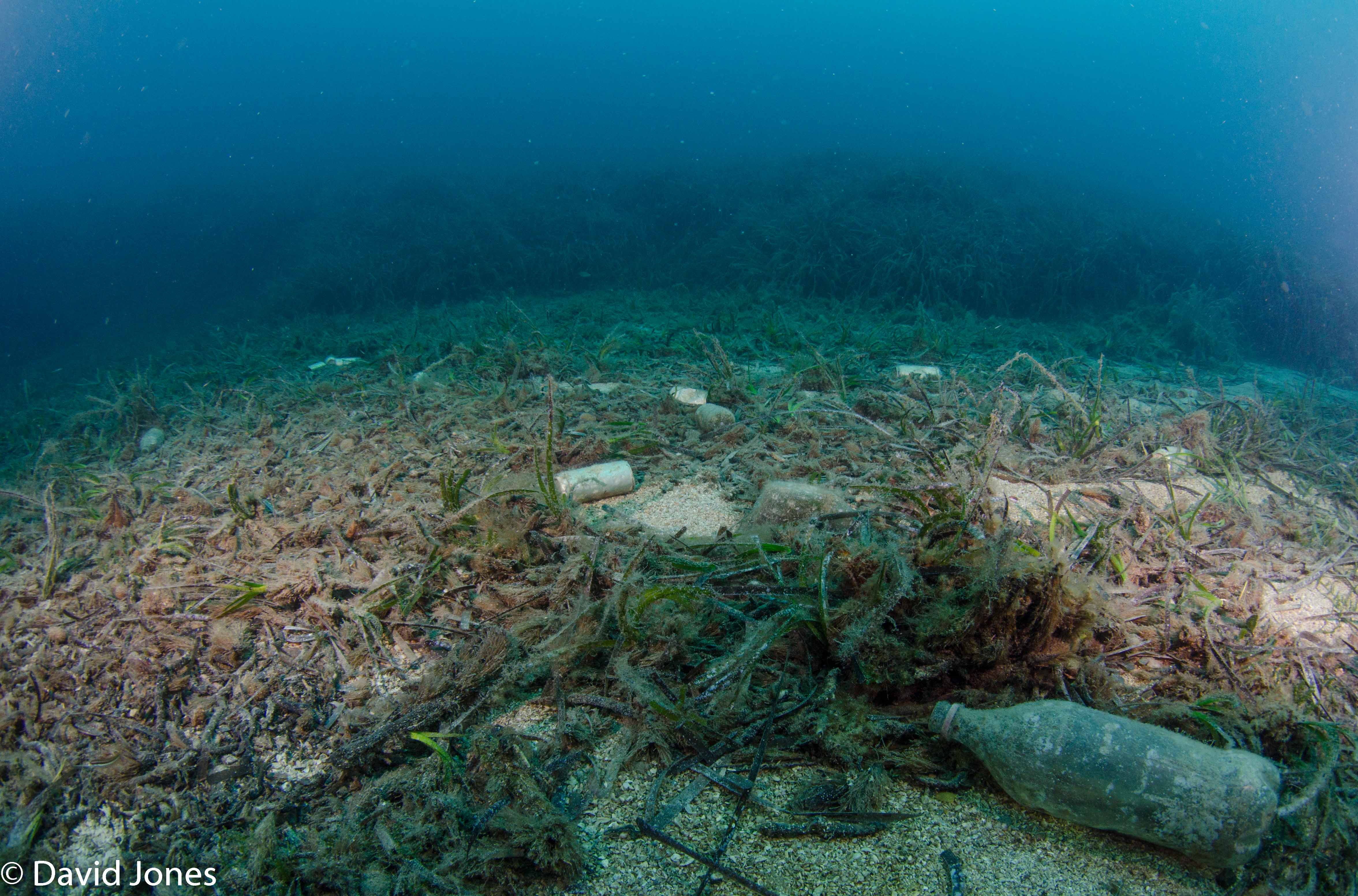

Habitat destruction is one of five global ecological pressures affecting the ocean, along with fishing pressure, climate change (including ocean acidification, water pollution and the introduction of alien species or genotypes.
Damage or destruction of habitats kills the plants and animals responsible for the habitat’s ecological functions and, in some cases, its survival and regeneration. This pressure focuses on destruction of intertidal habitats and two types of subtidal habitats, soft bottom and hard bottom. These habitats include coral reefs, sea grasses and mangrove forests, but do not include sea ice, which is accounted for elsewhere.
Coastal Pollution
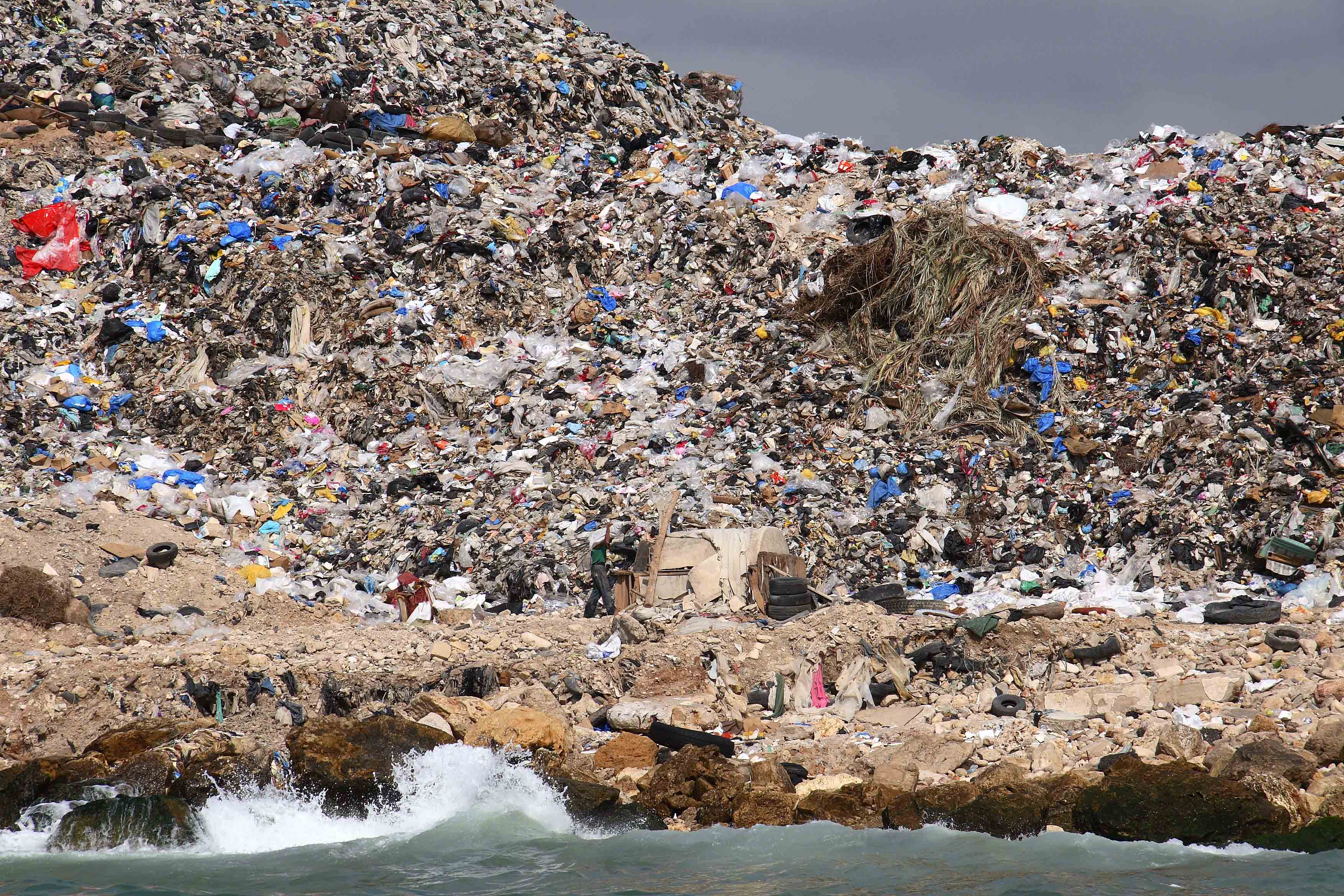

Coastal and estuarine ecosystems have been, and still are, heavily influenced by humans through pollution and habitat loss worldwide. Over 80% of all marine pollution originates from land-based sources which are primarily industrial, agricultural and urban [1]. Pollution accompanies most kinds of human activities, including offshore oil and gas production and marine oil transportation. Besides altering the marine environment, pollution also causes economic losses.